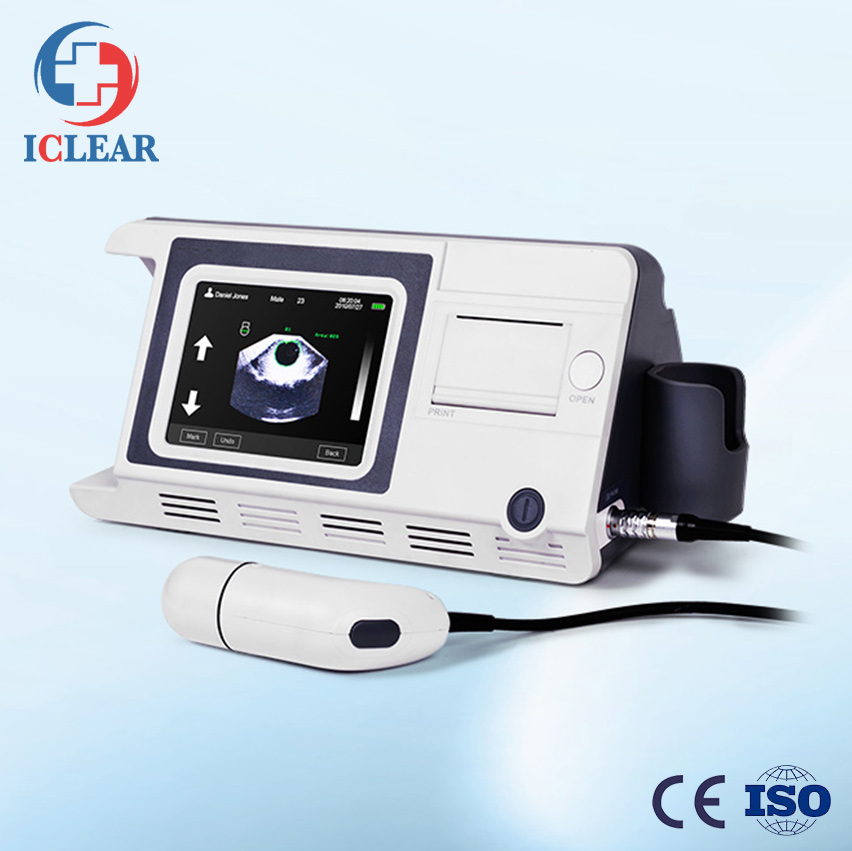
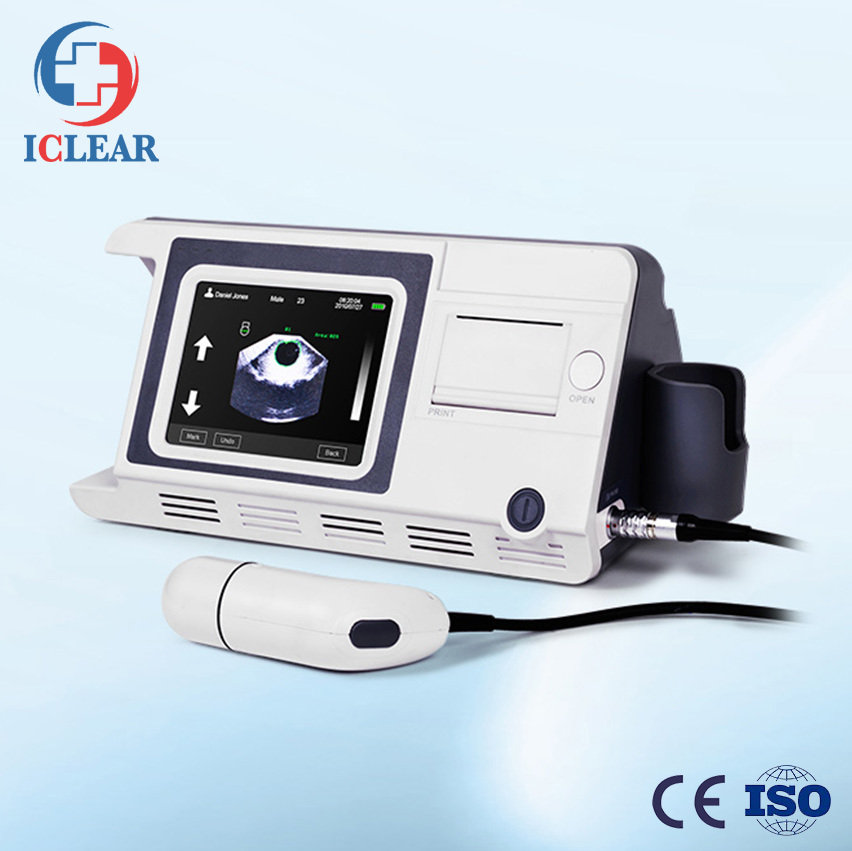
Method: 3D mechanical sector scanning
Probe Frequency: 2.5MHz
Scanning Depth: 20cm
Accuracy: ≤ ±15ml (0~100ml); ≤ ±15% (100~999ml)
Measuring Range: 0-999ml
Display: Touch screen color LCD
Power Supply: rechargeable lithium battery
Battery Capacity: 3000mAh, no less than 4 ours for normal use
Dimension: 337mm x 177mm x 155mm (L x W x H)
Net Weight: 2.2Kg (with battery and probe)
Preventing Cauti and Unnecessary Invasive Procedures Color Screen 3D Ultrasound Mechanical Sector Scanning Bladder Volume Scanner
CHO-BS6000
 Catheter-associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI) is a common and costly problem for hospitalized patients. Nurses have an important role to play in preventing CAUTI, and bladder scanners are now being frequently used by nurses at the bedside to prevent costly and invasive procedures, such as unnecessary catheterization and cystoscopy. Bladder scans are innovative tools that utilize technology to safely and accurately evaluate the need for catheterization.
Catheter-associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI) is a common and costly problem for hospitalized patients. Nurses have an important role to play in preventing CAUTI, and bladder scanners are now being frequently used by nurses at the bedside to prevent costly and invasive procedures, such as unnecessary catheterization and cystoscopy. Bladder scans are innovative tools that utilize technology to safely and accurately evaluate the need for catheterization.
A bladder scanner is a portable, hand-held ultrasound device, which can perform a quick, easy and non-invasive scan of the bladder. The scanner has an ultrasound probe and transducer to reflect sound waves from the patient's bladder to the scanner. Data is then transmitted to a computer in the handheld unit to automatically calculate the bladder volume. This ultrasound procedure is also referred to as bladder scanning.
Bladder scanning is painless for the patient and eliminates the risks associated with unnecessary catheterization. The entire scan takes only a couple of minutes to complete, does not require operation by a sonographer, and may prevent unnecessary invasive procedures.
There are several additional benefits to using a bladder scanner as a diagnostic tool. In the acute care setting, bladder scanners can assist in the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of post-operative urinary retention (POUR), and help prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections. In addition, studies have shown that bladder scanners are more effective than manual palpation in the assessment of postoperative bladder distention in the PACU (Society of Urologic Nurses and Associates [SUNA], 2011). The bladder scanner can be used to help identify bladder distention, identify causes of urinary frequency and bladder irritability, and is a useful tool to use in bladder training (Nurses Improving Care for Hospitalized Elders [NICHE], 2011). A bladder scanner may also be useful in assisting with the accurate assessment of a patient's hydration status.
Other uses of bladder scanners include the identification of a blocked Foley catheter, assessment of bladder status and function after the removal of an indwelling urinary catheter, and as a biofeedback tool in bladder training (SUNA, 2011).
Features
Method: 3D mechanical sector scanning
Probe Frequency: 2.5MHz
Scanning Depth: 20cm
Accuracy: ≤ ±15ml (0~100ml); ≤ ±15% (100~999ml)
Measuring Range: 0-999ml
Display: Touch screen color LCD
Power Supply: rechargeable lithium battery
Battery Capacity: 3000mAh, no less than 4 ours for normal use
Dimension: 337mm x 177mm x 155mm (L x W x H)
Net Weight: 2.2Kg (with battery and probe)
Standard Configuration
3D Probe
Battery
Battery Charger
Thermal Paper
Optional
Trolley
Carrying Case
Benefits
Urology, In-bed catheterization
Long-term Care, Postoperative Recovery
Neurology, Endocrinology, Emergency Room…